Now Reading: City-Scale Autonomous Orchestration: Predictive, Decentralized, and Continuously Optimized Urban Flows
-
01
City-Scale Autonomous Orchestration: Predictive, Decentralized, and Continuously Optimized Urban Flows
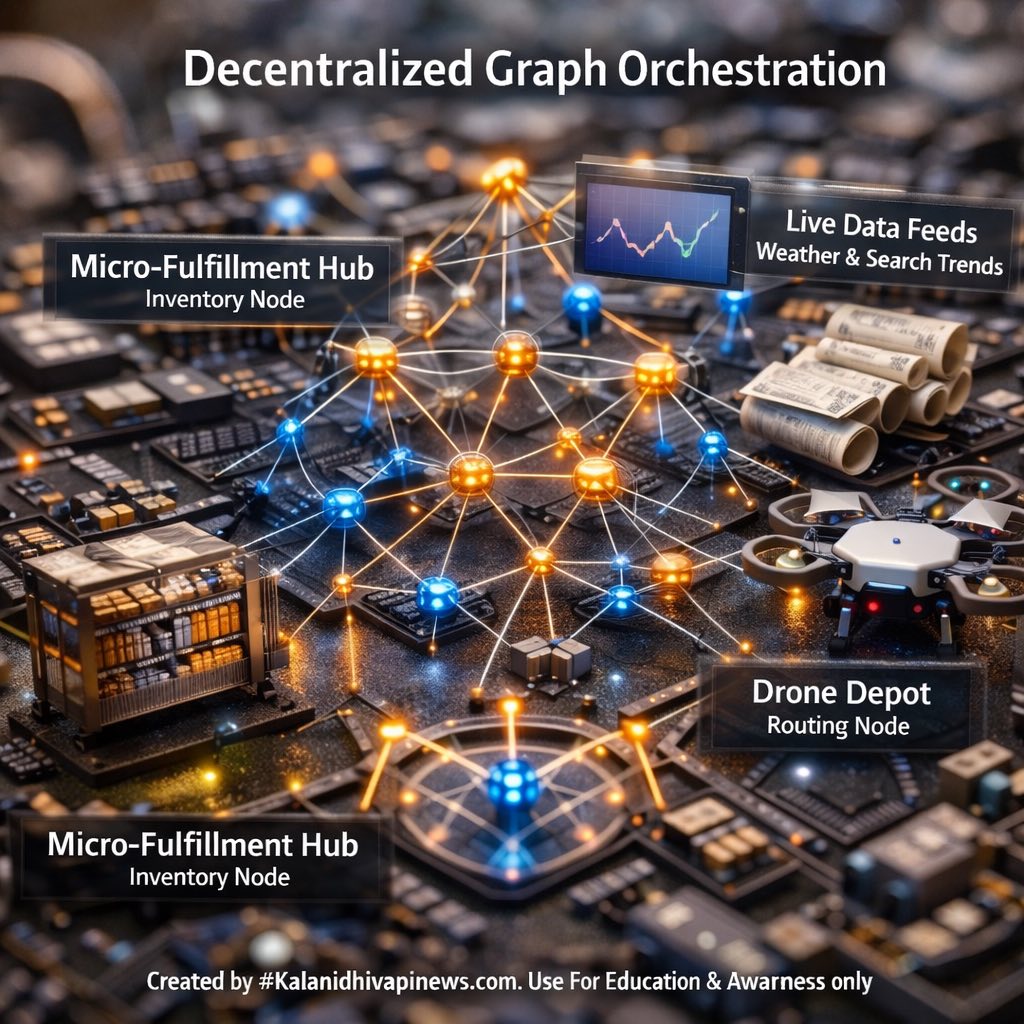
City-Scale Autonomous Orchestration: Predictive, Decentralized, and Continuously Optimized Urban Flows
City-scale orchestration coordinates multiple operational components into a single continuously optimized flow. It shifts systems from reactive responses to predictive, pre-emptive decision cycles. This enables smoother demand fulfillment across an entire urban network. It reduces fragmentation by aligning inventory, routing, and delivery states.
glossary: Orchestration means centralized coordination of distributed operational processes toward shared goals.
Predictive logic anticipates future demand before disruptions occur. It relies on historical and live signals to prepare resources in advance. This minimizes shortages and excess inventory across city zones. It improves service reliability and customer satisfaction.
glossary: Predictive refers to forecasting future conditions using data patterns.
Logistics manages the movement of goods across complex city environments. It integrates storage, transport, and delivery into a unified flow. Optimization at scale lowers costs and reduces congestion. It ensures timely fulfillment across diverse neighborhoods.
glossary: Logistics is the planning and execution of goods movement.
A unified framework allows design, deployment, and validation within one structure. It reduces integration friction between independent components. This supports faster iteration and safer scaling. It ensures consistency across all orchestration layers.
glossary: Framework is a structured system that supports development and operations.
A multi-agent setup divides responsibilities among specialized nodes. Each agent focuses on a distinct operational domain. Supervisory logic ensures alignment across agents. This improves resilience and scalability.
glossary: Multi-agent describes systems composed of multiple autonomous components.
Decentralization removes single points of failure. Local nodes can operate independently when needed. This improves fault tolerance at city scale. It enables faster localized decision-making.
glossary: Decentralized means control is distributed rather than centralized.
Graph architectures represent relationships between hubs and routes. They allow flexible linking of inventory and delivery nodes. Dynamic updates propagate efficiently across the network. This structure supports real-time optimization.
glossary: Graph is a network of nodes connected by edges.
Inventory management balances supply with anticipated demand. Predictive shifts prevent overstock and shortages. Real-time visibility enables faster adjustments. This improves capital efficiency.
glossary: Inventory refers to stored goods awaiting distribution.
Dynamic routing adapts paths as conditions change. Traffic density directly influences delivery plans. Continuous recomputation reduces delays. This ensures efficient city-wide movement.
glossary: Routing determines optimal paths for transportation.
State management preserves operational context across transitions. It prevents data loss during handoffs. Consistency ensures continuity of service. This is critical for multi-modal delivery systems.
glossary: State represents the current condition of a system.
Low latency enables rapid decision updates. Faster responses improve routing accuracy. Geographic proximity reduces delay. This enhances real-time orchestration.
glossary: Latency is the time delay between action and response.
Compliance ensures operations follow municipal regulations. Automated checks reduce human error. This prevents legal disruptions. It enables safe scaling of delivery networks.
glossary: Compliance is adherence to rules and regulations.
Circuit breakers isolate failures locally. They prevent cascading disruptions across the city. Recovery becomes faster and safer. System stability is preserved.
glossary: Circuit breaker is a mechanism that stops failure propagation.
Serverless patterns reduce infrastructure overhead. Resources scale automatically with demand. This supports agentic autonomy. Operational complexity is minimized.
glossary: Serverless refers to execution without managing servers.
Autonomy allows systems to act without hardcoded logic. Goals guide behavior rather than scripts. This improves adaptability. It supports evolving city dynamics.
glossary: Autonomy is the ability to operate independently.
Forecasting transforms historical data into future signals. It drives pre-emptive inventory movement. Accuracy improves planning confidence. It reduces reactive firefighting.
glossary: Forecasting predicts future trends from data.
Demand signals reflect consumer needs across time and space. Early detection enables proactive response. Balancing demand stabilizes operations. It improves service availability.
glossary: Demand is the need or desire for goods.
Repositioning moves inventory before shortages occur. It aligns stock with predicted demand. This reduces last-minute logistics stress. Efficiency improves across hubs.
glossary: Repositioning is relocating resources strategically.
Fulfillment completes the delivery promise to users. Speed and accuracy are critical. Integrated orchestration improves reliability. Customer trust increases.
glossary: Fulfillment is the process of completing orders.
Depots serve as operational nodes within the city. They enable rapid dispatch and recovery. Distributed depots reduce travel distance. They enhance resilience.
glossary: Depot is a facility for storage and dispatch.
Handoffs transfer responsibility between delivery modes. State continuity prevents errors. Smooth handoffs ensure service quality. Coordination is essential.
glossary: Handoff is the transfer of control or custody.
Optimization continuously improves system performance. Trade-offs are evaluated in real time. Resources are used efficiently. Outcomes improve at scale.
glossary: Optimization is making systems as effective as possible.
Inference enables rapid interpretation of live data. Faster inference supports timely decisions. Localized processing reduces delay. Accuracy improves responsiveness.
glossary: Inference is drawing conclusions from data.
Validation ensures designs work as intended. Early validation prevents systemic risks. Continuous testing improves reliability. Trust in deployment increases.
glossary: Validation confirms correctness and effectiveness.
Deployment transitions systems into live environments. Smooth deployment reduces downtime. Unified frameworks simplify rollout. Scalability is preserved.
glossary: Deployment is releasing systems into operation.
Debugging identifies and resolves architectural flaws. Early detection prevents propagation. System health improves over time. Reliability is strengthened.
glossary: Debugging is finding and fixing system issues.
Resilience allows systems to recover from disruptions. Local failures remain contained. Continuity of service is maintained. City operations remain stable.
glossary: Resilience is the ability to withstand and recover.
Scalability supports growth without performance loss. City expansion becomes manageable. Resources adapt to increasing demand. Long-term viability improves.
glossary: Scalability is the ability to grow efficiently.
Continuity ensures uninterrupted operational flow. State preservation enables smooth transitions. Users experience consistent service. Trust and reliability increase.
glossary: Continuity is sustained, uninterrupted operation.